Gelöste Aufgaben/JUMP/E-Motor and Drive-Train
Scope
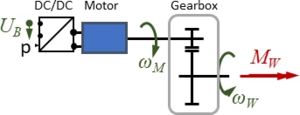
The Drive-Train consists of a DC/DC-converter, a DC Motor and a gear-box.
- DC/DC-converter: is supplied with the battery voltage UB, the output voltage is controlled by the driver via setpoint “p“.
- motor: is a standard DC brushed motor, the manufacturer provides only few information on its characteristics - we’ll need to improvise.
- gearbox: has a gear ratio of ratio of nG=100, its shaft rotates at speed ωW and delivers a torque MW to the front wheels.
The task is: provide a mathematical model for the drive train that accounts for load-alterations imposed by the driver. And we assume losses in the two converters - DC/DC and gearbox - to be negligible.
Structure

The drive train receives a "gas"-pedal position "p" from the driver and a battery-voltage UB.
It delivers a torque MW on the wheel and creates an electric current IM through the motor.
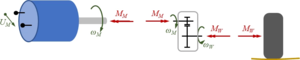
The sub-model consists of DC/DC-converter, Motor and gear-box:
DC/DC Converter
Losses in the DC/DC converter shall be small - so for input port “1“ and output port “2“ we obtain
- .
Let the “gas”-pedal-indicator “p“ control
with
Motor
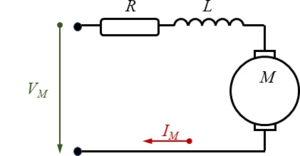
We use a common electric circuit representation for a series wound motor, the field coils are connected electrically in series with the armature coils, resistance R sums up all electrical losses in the motor.
Gearbox
Losses in the gearbox shall be small - so for input (ωM, MM) and output (ωW, MW) we obtain the fixed relation
- .
And we have only one differential equation for the electrical components:
- ,
the remaining equations are algebraic.
Model
Electrical Components
For the motor, we find with Kirchhoff's law that
with UR, UL being the differential voltage over resistance R and inductance L respectively. “e” is the back electromagnetic force with
and the electromotive force constant ke. Note the ωM is the differential rotational velocity between rotor and stator, i.e.
Employing
and using
with the armature constant kt, we have the complete set of equations.
From the above, we find
and additionally the algebraic equations
- .
/*******************************************************/
/* MAXIMA script */
/* version: wxMaxima 16.04.2 */
/* author: Andreas Baumgart */
/* last updated: 2021-02-08 */
/* ref: Modelling and Simulation (TUAS) */
/* description: virtual work of drive train electrics */
/*******************************************************/
/*******************************************************/
/* declarations */
/*******************************************************/
declare("φ", alphabetic);
declare("ψ", alphabetic);
declare("ω", alphabetic);
/*******************************************************/
/* kinematics */
/*******************************************************/
kirchhoff : [U[M] = p(t)*U[B],
U[B]*I[B] = U[M]*I[M],
U[M] = U[R] + U[L] + e,
e = k[e]*omega[M],
ω[M] = diff(ψ[M](t),t)+diff(φ(t),t),
U[R] = R*I[M](t),
U[L] = L * diff(I[M](t),t),
M[M] = k[t]*I[M](t)];
solve(kirchhoff[7], [diff(I[M](t),t)]);
tmp
Mechanical Components
Text
1+1=2
Variables
Parameter
>
References
- ...