Sources/Anleitungen/FEM-Formulierung für den Euler-Bernoulli-Balken: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
< Sources | Anleitungen
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 56: | Zeile 56: | ||
===Trial-Functions=== | ===Trial-Functions=== | ||
Die Koordinaten eines Finiten Elements sind | Die Koordinaten eines Finiten Elements sind | ||
Der Ansatz für die Näherung der Auslenkung ''w(x,t)'' ist | |||
::<math>\underline{Q}(t) = \left(\begin{array}{l}W_{i-1}(t)\\\Phi_{i-1}(t)\\W_{i}(t)\\\Phi_{i}(t)\end{array}\right)</math>. | |||
Der Ansatz für die Näherung der Auslenkung ''w(x,t)'' ist | |||
::<math>\displaystyle w(x,t) = \sum_{i=1}^4 Q_i(t) \cdot \phi_i(x)</math> | |||
Die Drehwinkel sind hier so gewählt, dass | Die Drehwinkel sind hier so gewählt, dass | ||
<math>\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx} w(x)|_{x=x_i} = \Phi_i</math>. | ::<math>\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx} w(x)|_{x=x_i} = \Phi_i</math>. | ||
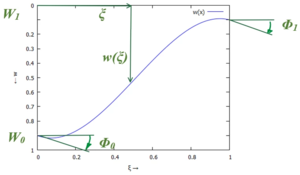
[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-FEM-01.png|mini|none|Nodal and independent Coordinates]] | |||
===Trialfunctions=== | |||
Die einzelnen Trial-Functions sind: | Die einzelnen Trial-Functions sind: | ||
<table class="wikitable" style="background-color:white | <table class="wikitable" style="background-color:white; margin-right:14px; | ||
"> | "> | ||
<tr><th>linker Rand (Knoten "''i-1''") | <tr><th>linker Rand (Knoten "''i-1''")</th><th>rechter Rand (Knoten "''i''")</th></tr> | ||
</th><th>rechter Rand (Knoten "''i''") | <tr><td>[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-FEM-02.png|mini|Trial-Function for ''W<sub>i-1</sub>'']]</td><td>[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-FEM-04.png|mini|Trial-Function for ''W<sub>i</sub>'']]</td></tr> | ||
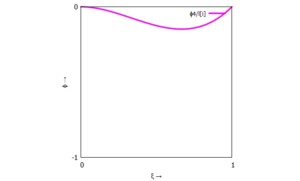
</th></tr> | <tr><th><math>\phi_1(\xi) = (\xi-1)^2 \cdot (2\;\xi+1)</math></th><th><math>\phi_3(\xi) = \xi^2 \cdot (3-2\;\xi)</math></th></tr> | ||
<tr><td></td><td></td></tr> | <tr><td>[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-FEM-03.png|mini|Trial-Function für ''Φ<sub>i-1</sub>'']]</td><td>[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-FEM-05.png|mini|Trial-Function für ''Φ<sub>i</sub>'']]</td></tr> | ||
<tr><th><math>\phi_2(\xi) = \ell_i \cdot \xi \cdot (\xi-1)^2</math></th><th><math>\phi_4(\xi) = \ell_i \cdot \xi^2 \cdot (\xi-1)</math></th></tr> | |||
</table> | </table> | ||
=== Faltungsintegrale === | |||
... für die symmetrische Massenmatrix. Tabelliert sind die Werte der Integrale | |||
::<math>\displaystyle \frac{m_{ij}}{\varrho A} = \int_0^\ell \phi_i \cdot \phi_j \; dx</math> | |||
<table class="wikitable" style="background-color:white; margin-right:14px;"> | |||
<tr><th> </th><th>''ϕ<sub>1</sub>''</th><th>''ϕ<sub>2</sub>''</th><th>''ϕ<sub>3</sub>''</th><th>''ϕ<sub>4</sub>''</th></tr> | |||
<tr><th>''ϕ<sub>1</sub>''</th><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr> | |||
<tr><th>''ϕ<sub>2</sub>''</th><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr> | |||
<tr><th>''ϕ<sub>3</sub>''</th><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr> | |||
<tr><th>''ϕ<sub>4</sub>''</th><td></td><td></td><td></td><td></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
.. fir die symmetrische Steifigkeitsmatrix. Tabelliert sind die Werte der Integrale | |||
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
| Zeile 95: | Zeile 113: | ||
[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-psi-1.png|rahmenlos|100x100px]] | [[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-psi-1.png|rahmenlos|100x100px]] | ||
[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-phi-2.png|rahmenlos|100x100px]][[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-psi-03.png|rahmenlos|100x100px]][[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-psi-04.png|rahmenlos|100x100px | [[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-phi-2.png|rahmenlos|100x100px]] | ||
[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-psi-03.png|rahmenlos|100x100px]] | |||
[[Datei:Anleitung-EBB-psi-04.png|rahmenlos|100x100px]] | |||
Version vom 19. April 2021, 13:00 Uhr
Diese Seite fasst die wichtigsten Ergebnisse für die FEM-Formulierung zum Euler-Bernoulli-Balken zusammen.
Maxima-Code
Hier finden Sie den Sourcecode für die Herleitung der Elelemt-Matrizen.
/*Maxima Quellcode für die Erzeugung Inhalte dieser Seite */
/* Maxima version 16.04.2*/
declare( "ℓ", alphabetic);
/*Trial-Fucntions*/
phi : [ (xi-1)^2*(2*xi+1),
ℓ[i]* xi *( xi-1)^2,
- xi^2 *(2*xi-3),
ℓ[i]* xi^2 *( xi-1)];
/* depict independant and dependant coordinates */
preamble: "set yrange [] reverse";
plot2d(subst([ℓ[i]=1],[0.9,1/2,0.1,1/3].phi),[xi,0,1],
[x,0,1], [legend, "w(x)"],
[xlabel, "ξ →"], [ylabel, "← w"],
[gnuplot_preamble, preamble]);
/* plot trial-functions parameters */
scale: [1,1/ℓ[i],1,1/ℓ[i]];
colours: [blue, red, green, magenta];
legends: ["ϕ1","ϕ2/ℓ[i]","ϕ3","ϕ4/ℓ[i]"];
for j:1 thru 4 do
(plot2d(scale[j]*phi[j],[xi,0,1], [xlabel,"ξ →"],[ylabel,"ϕ →"], [legend,legends[j]],[color,colours[j]], [style, [lines,3]], same_xy,
[gnuplot_preamble, "set xtics 1;set ytics 1;set tics font \",11\""]))$
/* Element-Mass Matrix */
M[i] : funmake('matrix,makelist(makelist(rho*A*integrate(phi[j]*phi[k],xi,0,1)*ℓ[i],j,1,4),k,1,4));
/* (rho*A*ℓ[i])*matrix([13/35,(11*ℓ[i])/210,9/70,-(13*ℓ[i])/420],
[(11*ℓ[i])/210,ℓ[i]^2/105,(13*ℓ[i])/420,-ℓ[i]^2/140],
[9/70,(13*ℓ[i])/420,13/35,-(11*ℓ[i])/210],
[-(13*ℓ[i])/420,-ℓ[i]^2/140,-(11*ℓ[i])/210,ℓ[i]^2/105]) */
/* Element-Striffness Matrix */
K[i] : funmake('matrix,makelist(makelist(EI*integrate(diff(phi[j],xi,2)/ℓ[i]^2*diff(phi[k],xi,2)/ℓ[i]^2,xi,0,1)*ℓ[i],j,1,4),k,1,4));
/* (EI/ℓ[i]^3)*matrix([12,6*ℓ[i],-12,6*ℓ[i]],
[6*ℓ[i],4*ℓ[i]^2,-6*ℓ[i],2*ℓ[i]^2],
[-12,-6*ℓ[i],12,-6*ℓ[i]],
[6*ℓ[i],2*ℓ[i]^2,-6*ℓ[i],4*ℓ[i]^2]) */
Trial-Functions
Die Koordinaten eines Finiten Elements sind
- .
Der Ansatz für die Näherung der Auslenkung w(x,t) ist
Die Drehwinkel sind hier so gewählt, dass
- .
Trialfunctions
Die einzelnen Trial-Functions sind:
| linker Rand (Knoten "i-1") | rechter Rand (Knoten "i") |
|---|---|
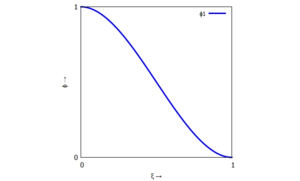 | 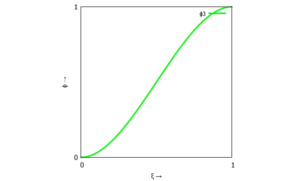 |
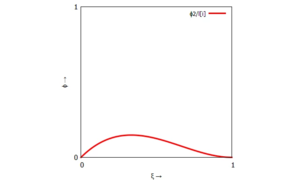 |  |
Faltungsintegrale
... für die symmetrische Massenmatrix. Tabelliert sind die Werte der Integrale
| ϕ1 | ϕ2 | ϕ3 | ϕ4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ϕ1 | ||||
| ϕ2 | ||||
| ϕ3 | ||||
| ϕ4 |
.. fir die symmetrische Steifigkeitsmatrix. Tabelliert sind die Werte der Integrale
Links
- ...
Literature
- ...