Gelöste Aufgaben/Kw98: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| (8 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
[[Category:Gelöste Aufgaben]] | [[Category:Gelöste Aufgaben]] | ||
[[Category:Analytische Lösung]] | [[Category:Analytische Lösung]] | ||
[[Category:Randwertproblem]] | [[Category:Randwertproblem]] | ||
[[Category:Biege-Belastung]] | |||
[[Category:Biege-Belastung | |||
[[Category:Euler-Bernoulli-Balken]] | [[Category:Euler-Bernoulli-Balken]] | ||
[[Category:Maxima]] | [[Category:Maxima]] | ||
==Aufgabenstellung== | ==Aufgabenstellung== | ||
Ein Stab ''ABC'' ist durch eine lineare veränderliche Streckenlast ''q'' mit den Eckwerten ''q<sub>A</sub>'' in ''A'' und ''q<sub>B</sub>'' in ''B'' sowie dem Moment ''M<sub>B</sub>'' in ''B'' belastet. Der Stab (E-Modul: ''E'') besteht aus zwei Sektionen mit den Längen ''l<sub>1</sub>'' bzw. ''l<sub>2</sub>'' sowie den Flächenmomenten ''I<sub>1</sub>'' bzw. ''I<sub>2</sub>''. Der Stab ist in ''A'' durch ein gelenkiges Festlager, in ''C'' durch eine Schiebehülse gelagert, in ''B'' sind die beiden Sektionen fest miteinander verbunden. Die Feder in ''A'' ist eine Drehfester mit Steifigkeit ''K<sub>A</sub>'', die Federn in ''B'' und ''C'' sind Translationsfedern mit den Steifigkeiten ''k<sub>B</sub>, k<sub>C</sub>''. | |||
<onlyinclude> | <onlyinclude> | ||
[[Datei: | [[Datei:Kw98-01.png|alternativtext=|links|mini|250x250px|Lageplan]] | ||
Gesucht ist | Gesucht ist die analytische Lösung für den Euler-Bernoulli-Balken. | ||
</onlyinclude> | </onlyinclude> | ||
[[Datei:Kw98-02.png|mini|Systemparameter]] | |||
Ermitteln Sie für ein Euler-Bernoulli-Modell die analytischen Verläufe der Schnittgrößen und Verschiebungen im Balken für diese Parameter: | |||
== Lösung mit Maxima == | == Lösung mit Maxima == | ||
== | Die Aufgabe ist ein klassisches Randwertproblem: | ||
# zwei Gebiete, in denen ein Euler-Bernoulli-Balken in AB und BC durch eine Streckenlast ''q'' belastet ist (in Bereich II ist die Streckenlast allerdings Null) und somit durch die Differentialbeziehung<blockquote><math>E\; I_i w_i^{IV}(x_i) = q(x_i) ,\;\; i=\{1,2\}</math></blockquote>berschrieben wird. | |||
# Rand- und Übergangsbedingungen in den Punkten A, B, C | |||
Wir verwenden ''x<sub>i</sub>'' und ''ξ<sub>i</sub>'' als Koordinaten je Bereich, in der Übersicht sieht das Randwertproblem so aus:<table class="wikitable" style="background-color:white;"> | |||
<tr><th>Rand<br />A</th><th>Bereich I</th><th>Übergang<br />B</th><th>Bereich II</th><th>Rand<br />C</th></tr> | |||
<tr><td></td><td>[[Datei:Kw98-11AB.png|rahmenlos|alternativtext=|200x200px]]</td><td></td><td>[[Datei:Kw98-11BC.png|rahmenlos|alternativtext=|150x150px]]</td><td></td></tr> | |||
<tr><td>[[Datei:Kw98-11A.png|116x116px|rahmenlos|alternativtext=]]</td><td></td><td>[[Datei:Kw98-11B.png|rahmenlos|alternativtext=|128x128px]]</td><td></td><td>[[Datei:Kw98-11C.png|rahmenlos|alternativtext=|140x140px]] | |||
</td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------> | <!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------> | ||
{{MyCodeBlock|title= | {{MyCodeBlock|title=Header | ||
|text= | |text= | ||
Diese Aufgabe mit der [[Randwertprobleme/Methoden zur Lösung von Randwertproblemen/Finite Elemente Methode|Methode der Finiten Elemente]] in [[Gelöste Aufgaben/Kw96|KW96]] gelöst. | |||
|code= | |code= | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lisp" line start=1> | <syntaxhighlight lang="lisp" line start=1> | ||
1 | /*******************************************************/ | ||
/* MAXIMA script */ | |||
/* version: wxMaxima 15.08.2 */ | |||
/* author: Andreas Baumgart */ | |||
/* last updated: 2017-09-06 */ | |||
/* ref: TM-C, Labor 1 */ | |||
/* description */ | |||
/* */ | |||
/*******************************************************/ | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
}} | }} | ||
<table class="wikitable" style="background-color:white; | <!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------> | ||
"> | {{MyCodeBlock|title=Declarations | ||
<tr>< | |text= | ||
<tr><td></td><td></td></tr> | Wir definieren die Parameter | ||
::<math>\begin{array}{l}q_{A}=\frac{3\cdot kN}{m},\\l_{1}=\frac{7\cdot m}{10}, \\EI_{1}=33600\; N\; {{m}^{2}},\\{{l}_{2}}=\frac{21\; m}{40},\\EI_{2}=16800\; N\;{{m}^{2}},\\{{K}_{A}}=96\;kN\; m,\\{{k}_{C}}=\frac{22\;kN}{m},\\{{k}_{B}}=\frac{98\;kN}{m},\\{{q}_{B}}=\frac{12\; N}{mm},\\{{M}_{B}}=1470\; Nm\end{array}</math>. | |||
und die Formfunktionen für die Streckenlast | |||
::<math>\begin{array}{l}{{\phi}_{0}}\left( \xi\right) :=1-\xi\\{{\phi}_{1}}\left( \xi\right) :=\xi\end{array}</math>. | |||
|code= | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lisp" line start=1> | |||
/* system parameter */ | |||
units : [mm = m/1000, cm = m/100]; | |||
params : [q[A]=3*N/mm, l[1]=700*mm, EI[1] = 2.1*10^11*N/m^2 * 3*cm*(4*cm)^3/12]; | |||
simple : [l[2] = 3/4*l[1], EI[2] = EI[1]/2, | |||
K[A]=2*EI[1]/l[1], k[C] = 512/229*EI[1]/l[1]^3, k[B] = EI[1]/l[1]^3, | |||
q[B] = 4*q[A], M[B] = q[A]*l[1]^2]; | |||
params : append(params,makelist(lhs(simple[i])=subst(params,rhs(simple[i])),i,1,length(simple))); | |||
params : subst(units,params); | |||
/* form - functions */ | |||
phi[0](xi) := 1 - xi; | |||
phi[1](xi) := xi; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
}} | |||
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------> | |||
{{MyCodeBlock|title=Formfunctions | |||
|text= | |||
In Bereich I und II gilt dieselbe Bewegungs-Differentialgleichung | |||
::<math>E\; I_i w_i^{IV}(x_i) = q(x_i) ,\;\; i=\{1,2\} \text{ mit } q(x_i) = q_0\cdot\phi_0(\xi) + q_1\cdot\phi_1(\xi)</math>, | |||
die wir durch Integration lösen und dann bereichsweise anpassen. | |||
So gilt für Bereich II: ''q<sub>0</sub> = 0'' und ''q<sub>1</sub> = 0''. | |||
Die allgemeine Lösung ist mit | |||
::<math>\displaystyle \phi_i(x) = \frac{dw(x)}{dx}</math> | |||
... für Bereich I: | |||
::<math>\begin{array}{l} {{w}_{1}}\left( x\right) :=\frac{120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,0}}+120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,1}}\cdot x+60\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,2}}\cdot {{x}^{2}}+20\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,3}}\cdot {{x}^{3}}+5\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{x}^{4}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}+{{x}^{5}}\cdot \left( {{q}_{B}}-{{q}_{A}}\right) }{120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}\\ {{\phi}_{1}}\left( x\right) :=\frac{120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,1}}+120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,2}}\cdot x+60\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,3}}\cdot {{x}^{2}}+20\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{x}^{3}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}+5\cdot {{x}^{4}}\cdot \left( {{q}_{B}}-{{q}_{A}}\right) }{120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}\\ {{M}_{1}}\left( x\right) :=-\frac{120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,2}}+120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,3}}\cdot x+60\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{x}^{2}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}+20\cdot {{x}^{3}}\cdot \left( {{q}_{B}}-{{q}_{A}}\right) }{120\cdot {{l}_{1}}}\\ {{Q}_{1}}\left( x\right) :=-\frac{120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,3}}+120\cdot {{l}_{1}}\cdot x\cdot {{q}_{A}}+60\cdot {{x}^{2}}\cdot \left( {{q}_{B}}-{{q}_{A}}\right) }{120\cdot {{l}_{1}}} \end{array}</math> | |||
... für Bereich II: | |||
::<math>\begin{array}{l} {{w}_{2}}\left( x\right) :=\frac{120\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,0}}+120\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,1}}\cdot x+60\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,2}}\cdot {{x}^{2}}+20\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,3}}\cdot {{x}^{3}}}{120\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}\\ {{\phi}_{2}}\left( x\right) :=\frac{120\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,1}}+120\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,2}}\cdot x+60\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,3}}\cdot {{x}^{2}}}{120\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}\\ {{M}_{2}}\left( x\right) :=-\frac{120\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,2}}+120\cdot {{l}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,3}}\cdot x}{120\cdot {{l}_{2}}}\\ {{Q}_{2}}\left( x\right) :=-{{C}_{2,3}} \end{array}</math>. | |||
|code= | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lisp" line start=1> | |||
/* solve ....*/ | |||
dgl : EI[i]*diff(w(x),x,4) = q[0]*phi[0](x/l[i]) + q[1]*phi[1](x/l[i]); | |||
/* generic solution */ | |||
displ : solve(integrate(integrate(integrate(integrate(dgl,x),x),x),x),w(x)); | |||
sections: [[i=1, %c4=C[1,0], %c3=C[1,1], %c2=C[1,2], %c1=C[1,3], q[0]=q[A], q[1]=q[B]], | |||
[i=2, %c4=C[2,0], %c3=C[2,1], %c2=C[2,2], %c1=C[2,3], q[0]= 0 , q[1]= 0 ]]; | |||
/* section I */ | |||
define( w[1](x), subst(sections[1],subst(displ,w(x)))); | |||
define(Phi[1](x), diff(w[1](x),x )); | |||
define( M[1](x), -EI[1]*diff(w[1](x),x,2)); | |||
define( Q[1](x), -EI[1]*diff(w[1](x),x,3)); | |||
/* section II */ | |||
define( w[2](x), subst(sections[2],subst(displ,w(x)))); | |||
define(Phi[2](x), diff(w[2](x),x )); | |||
define( M[2](x), -EI[2]*diff(w[2](x),x,2)); | |||
define( Q[2](x), -EI[2]*diff(w[2](x),x,3)); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
}} | |||
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------> | |||
{{MyCodeBlock|title=Boundary Conditions | |||
|text= | |||
Für die 2*4 = 8 Integrationskonstanten | |||
::<math>\left[ C_{1,0},C_{1,1},C_{1,2},C_{1,3},C_{2,0},C_{2,1},C_{2,2},C_{2,3}\right]</math> | |||
suchen wir jetzt die passenden Gleichungen aus Rand- und Übergangsbedingungen. | |||
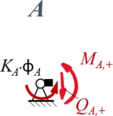
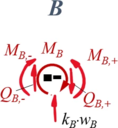
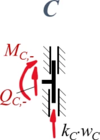
Zur besseren Übersicht nennen wir die Schnitt-Momente und -Kräfte nach den jeweiligen Knotenpunkten A, B, C und fügen als Index ein + / - hinzu, um die Seite (+: rechts vom Knoten, -: links vom Knoten) zu kennzeichnen. | |||
====Aus Rand "A"==== | |||
<table class="wikitable" style="background-color:white;"> | |||
<tr><td>[[Datei:Kw98-11A.png|rahmenlos|alternativtext=|134x134px]] | |||
</td><td>''Geometrische Randbedingungen'' | |||
# <math>w_1(0)=0</math> | |||
''Kraft- und Momenten-Randbedingungen'' | |||
#<math>K_A\cdot \phi_A + M_{A,+} = 0 \text{ mit } M_{A,+} = - EI_1\cdot w''(x)|_{x=0}</math> | |||
</td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
====Aus Übergang "B"==== | |||
<table class="wikitable" style="background-color:white;"> | |||
<tr><td>[[Datei:Kw98-11B.png|rahmenlos|alternativtext=|162x162px]] | |||
</td><td>''Geometrische Randbedingungen'' | |||
#<math>w_1(\ell_1)=w_2(\ell_1)</math> | |||
#<math>\phi_1(\ell_1) = \phi_2(\ell_1)</math> | |||
''Kraft- und Momenten-Randbedingungen'' | |||
#<math>-M_{B,-} - M_{B} + M_{B,+} = 0</math> | |||
#<math>-Q_{B,-}-k_B\cdot w_B + -Q_{B,+} = 0</math> | |||
</td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
====Aus Rand "C"==== | |||
<table class="wikitable" style="background-color:white;"> | |||
<tr><td>[[Datei:Kw98-11C.png|rahmenlos|alternativtext=|154x154px]] | |||
</td><td>''Geometrische Randbedingungen'' | |||
#<math>\phi_2(\ell_2)=0</math> | |||
''Kraft- und Momenten-Randbedingungen'' | |||
#<math>-Q_{C,-} -k_C\cdot w_C = 0</math> | |||
</td></tr> | |||
</table> | </table> | ||
Und das liefert das Gleichungssystem aus 8 Gleichungen | |||
::<math>\begin{pmatrix}\frac{{{C}_{1,0}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}=0\\ \frac{{{C}_{1,1}}\cdot {{K}_{A}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}-{{C}_{1,2}}=0\\ \frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{4}}\cdot {{q}_{B}}}{120\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{4}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}}{30\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{3}}\cdot {{C}_{1,3}}}{6\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{2}}\cdot {{C}_{1,2}}}{2\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,1}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{C}_{1,0}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}=\frac{{{C}_{2,0}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}\\ \frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{3}}\cdot {{q}_{B}}}{24\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{3}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}}{8\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{2}}\cdot {{C}_{1,3}}}{2\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,2}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}+\frac{{{C}_{1,1}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}=\frac{{{C}_{2,1}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}\\ \frac{{{\ell}_{1}}\cdot {{q}_{B}}}{2}-\frac{{{C}_{2,0}}\cdot {{k}_{B}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}}{2}-{{C}_{2,3}}+{{C}_{1,3}}=0\\ -{{M}_{B}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{2}}\cdot {{q}_{B}}}{6}+\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{2}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}}{3}-{{C}_{2,2}}+{{\ell}_{1}}\cdot {{C}_{1,3}}+{{C}_{1,2}}=0\\ \frac{{{\ell}_{2}^{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,3}}}{2\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}+\frac{{{\ell}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,2}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}+\frac{{{C}_{2,1}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}=0\\ -\frac{{{\ell}_{2}^{3}}\cdot {{C}_{2,3}}\cdot {{k}_{C}}}{6\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}-\frac{{{\ell}_{2}^{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,2}}\cdot {{k}_{C}}}{2\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}-\frac{{{\ell}_{2}}\cdot {{C}_{2,1}}\cdot {{k}_{C}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}-\frac{{{C}_{2,0}}\cdot {{k}_{C}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}+{{C}_{2,3}}=0\end{pmatrix} | |||
</math>. | |||
für die Integrationskonstanten. | |||
|code= | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lisp" line start=1> | |||
/* integration constants */ | |||
ICs : [C[1,0],C[1,1],C[1,2],C[1,3],C[2,0],C[2,1],C[2,2],C[2,3]]; | |||
/* boundary conditions */ | |||
node[A]: [ w[1](0) = 0, | |||
K[A]*Phi[1](0)+M[1](0) = 0]; | |||
node[B]: [ w[1](l[1]) = w[2](0), | |||
Phi[1](l[1]) = Phi[2](0), | |||
-Q[1](l[1]) -k[B]*w[2](0) +Q[2](0) = 0, | |||
-M[1](l[1]) -M[B]+M[2](0) = 0]; | |||
node[C]: [ Phi[2](l[2]) = 0, | |||
-Q[2](l[2]) - k[C]*w[2](l[2]) = 0]; | |||
BCs : expand(append(node[A],node[B],node[C])); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
}} | |||
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------> | |||
{{MyCodeBlock|title=Prepare for Solver | |||
|text= | |||
Das Gleichungssystem wollen wir als | |||
::<math>\underline{\underline{A}}\cdot\underline{x}= \underline{b}</math> | |||
schreiben, also | |||
::<math>\begin{pmatrix}\frac{1}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & \frac{{{K}_{A}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & -1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ \frac{1}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & \frac{{{\ell}_{1}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & \frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{2}}}{2\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & \frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{3}}}{6\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & -\frac{1}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}} & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & \frac{1}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & \frac{{{\ell}_{1}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & \frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{2}}}{2\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}} & 0 & -\frac{1}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}} & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & -\frac{{{k}_{B}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}} & 0 & 0 & -1\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & {{\ell}_{1}} & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \frac{1}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}} & \frac{{{\ell}_{2}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}} & \frac{{{\ell}_{2}^{2}}}{2\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & -\frac{{{k}_{C}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}} & -\frac{{{\ell}_{2}}\cdot {{k}_{C}}}{{{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}} & -\frac{{{\ell}_{2}^{2}}\cdot {{k}_{C}}}{2\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}} & -\frac{{{\ell}_{2}^{3}}\cdot {{k}_{C}}-6\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}{6\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{2}}}\end{pmatrix}\cdot\underline{x}=\begin{pmatrix}0\\ 0\\ -\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{4}}\cdot {{q}_{B}}}{120\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}-\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{4}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}}{30\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}\\ -\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{3}}\cdot {{q}_{B}}}{24\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}-\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{3}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}}{8\cdot {{\mathit{EI}}_{1}}}\\ -\frac{{{\ell}_{1}}\cdot {{q}_{B}}}{2}-\frac{{{\ell}_{1}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}}{2}\\ {{M}_{B}}-\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{2}}\cdot {{q}_{B}}}{6}-\frac{{{\ell}_{1}^{2}}\cdot {{q}_{A}}}{3}\\ 0\\ 0\end{pmatrix} | |||
</math> | |||
Die Matrix-Elemente sind für die Koeffizientenmatrix | |||
::<math>\begin{array}{l} a_{1,1} = 1/EI_{1}\\ a_{2,2} = K_{A}/EI_{1}\\ a_{2,3} = -1\\ a_{3,1} = 1/EI_{1}\\ a_{3,2} = \ell_{1}/EI_{1}\\ a_{3,3} = \ell_{1}^2/(2\cdot EI_{1})\\ a_{3,4} = \ell_{1}^3/(6\cdot EI_{1})\\ a_{3,5} = -1/EI_{2}\\ a_{4,2} = 1/EI_{1}\\ a_{4,3} = \ell_{1}/EI_{1}\\ a_{4,4} = \ell_{1}^2/(2\cdot EI_{1})\\ a_{4,6} = -1/EI_{2}\\ a_{5,4} = 1\\ a_{5,5} = -k_{B}/EI_{2}\\ a_{5,8} = -1\\ a_{6,3} = 1\\ a_{6,4} = \ell_{1}\\ a_{6,7} = -1\\ a_{7,6} = 1/EI_{2}\\ a_{7,7} = \ell_{2}/EI_{2}\\ a_{7,8} = \ell_{2}^2/(2\cdot EI_{2})\\ a_{8,5} = -k_{C}/EI_{2}\\ a_{8,6} = -(\ell_{2}\cdot k_{C})/EI_{2}\\ a_{8,7} = -(\ell_{2}^2\cdot k_{C})/(2\cdot EI_{2})\\ a_{8,8} = -(\ell_{2}^3\cdot k_{C}-6\cdot EI_{2})/(6\cdot EI_{2})\\ \end{array}</math> | |||
und für die rechte Seite | |||
::<math>\begin{array}{l} b_{1} = 0\\ b_{2} = 0\\ b_{3} = (-(\ell_{1}^4\cdot q_{B})/(120\cdot EI_{1}))-(\ell_{1}^4\cdot q_{A})/(30\cdot EI_{1})\\ b_{4} = (-(\ell_{1}^3\cdot q_{B})/(24\cdot EI_{1}))-(\ell_{1}^3\cdot q_{A})/(8\cdot EI_{1})\\ b_{5} = (-(\ell_{1}\cdot q_{B})/2)-(\ell_{1}\cdot q_{A})/2\\ b_{6} = M_{B}-(\ell_{1}^2\cdot q_{B})/6-(\ell_{1}^2\cdot q_{A})/3\\ b_{7} = 0\\ b_{8} = 0 \end{array}</math>. | |||
|code= | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lisp" line start=1> | |||
/* augmented coeff matrix */ | |||
ACM: augcoefmatrix(BCs,ICs); | |||
AA : submatrix(ACM,9); | |||
bb : - col(ACM,9); | |||
for i: 1 thru 8 do | |||
print(simplode(["b[",i,"] = ", string(bb[i][1])]))$ | |||
for i: 1 thru 8 do | |||
for j: 1 thru 8 do | |||
if not AA[i][j] = 0 then | |||
print(simplode(["A[",i,",",j,"] = ", string(AA[i][j])]))$ | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
}} | |||
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------> | |||
{{MyCodeBlock|title=Solving | |||
|text= | |||
Das Lösen des Gleichungssystems liefert | |||
::<math>\begin{array}{l} {{C}_{1,0}}=0,\\{{C}_{1,1}}=246.1 \; N {{m}^{2}},\\{{C}_{1,2}}=703.2\; N m,\\{{C}_{1,3}}=-2404.3\; N,\\{{C}_{2,0}}=127.6 \; N m^3,\\{{C}_{2,1}}=224.7\; N m^2,\\{{C}_{2,2}}=-979.8 \; N m,\\{{C}_{2,3}}=2101.8 N \end{array}</math>. | |||
|code= | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lisp" line start=1> | |||
/* solving */ | |||
D : ratsimp(determinant(AA))$ | |||
[ P, L, U] : ratsimp(get_lu_factors(lu_factor(AA)))$ | |||
cc : ratsimp(linsolve_by_lu(AA,bb)[1])$ | |||
sol : makelist(ICs[i] = cc[i][1],i,1,8)$ | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
}} | |||
<!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------> | |||
{{MyCodeBlock|title=Post-Processing | |||
|text= | |||
Und die Ergebnisse können wir uns anschauen ... | |||
==== ... für w(x): ==== | |||
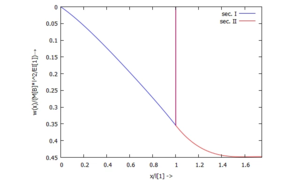
[[Datei:Kw98-21.png|mini|Biegelinie ''w(x)''|alternativtext=|ohne]] | |||
==== ... für ''Φ(x)'': ==== | |||
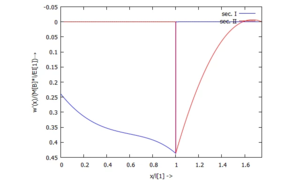
[[Datei:Kw98-22.png|mini|Kippung ''w'(x)''|alternativtext=|ohne]] | |||
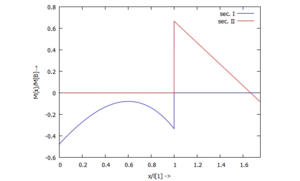
==== ... für M(x): ==== | |||
[[Datei:Kw98-23.png|mini|Biegemoment M(x)|alternativtext=|ohne]] | |||
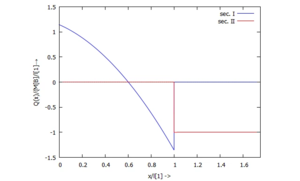
==== ... für Q(x): ==== | |||
[[Datei:Kw98-24.png|mini|Querkraft ''Q(x)''|alternativtext=|ohne]] | |||
====... für die Lager-Reaktionskräfte:==== | |||
::<math>\begin{array}{l} {{A}_{z}}=2404.3 N,\\{{M}_{A}}=703.2 Nm,\\{{B}_{z}}=743.9 N,\\{{C}_{z}}=2101.8 N,\\{{M}_{C}}=-123.7 Nm\end{array}</math> | |||
|code= | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lisp" line start=1> | |||
/* bearing forces and moments */ | |||
reactForces: [A[z]=Q[1](0), | |||
M[A] = K[A]*Phi[1](0), | |||
B[z] = k[B]*w[2](0), | |||
C[z] = k[C]*w[2](l[2]), | |||
M[C] = M[2](l[2])]; | |||
expand(subst(params,subst(sol, reactForces))); | |||
/* plot displacements */ | |||
fcts: [[ w [1](x), w [2](x-l[1])], | |||
[Phi[1](x),Phi[2](x-l[1])], | |||
[ M [1](x), M [2](x-l[1])], | |||
[ Q [1](x), Q [2](x-l[1])]]; | |||
facts: [EI[1]/(l[1]^4*q[A]),EI[1]/(l[1]^3*q[A]),1/(l[1]^2*q[A]),1/(l[1]^1*q[A])]; | |||
subst(M[B]/l[1]^2,q[A],facts); | |||
textlabels : ["w(x)/(M[B]*l^2/EI[1])→", "w'(x)/(M[B]*l/EI[1])→", "M(x)/M[B]→", "Q(x)/(M[B]/l[1]→"]; | |||
for i: 1 thru 4 do( | |||
f : expand(subst(simple,subst(xi*l[1],x,facts[i]*[subst(sol, fcts[i][1]), | |||
subst(sol, fcts[i][2])]))), | |||
f1 : f[1], f2 : f[2], | |||
toplot : [if xi<=1 then f1 else 0, | |||
if xi < 1 then 0 else f2], | |||
plot2d(toplot,[xi,0,1+subst(simple,l[2]/l[1])], [legend, "sec. I", "sec. II"], | |||
[gnuplot_preamble, "set yrange [] reverse"] , | |||
[xlabel, "x/l[1] ->"], | |||
[ylabel, textlabels[i]]))$ | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
}} | |||
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 31. März 2021, 12:30 Uhr
Aufgabenstellung
Ein Stab ABC ist durch eine lineare veränderliche Streckenlast q mit den Eckwerten qA in A und qB in B sowie dem Moment MB in B belastet. Der Stab (E-Modul: E) besteht aus zwei Sektionen mit den Längen l1 bzw. l2 sowie den Flächenmomenten I1 bzw. I2. Der Stab ist in A durch ein gelenkiges Festlager, in C durch eine Schiebehülse gelagert, in B sind die beiden Sektionen fest miteinander verbunden. Die Feder in A ist eine Drehfester mit Steifigkeit KA, die Federn in B und C sind Translationsfedern mit den Steifigkeiten kB, kC.
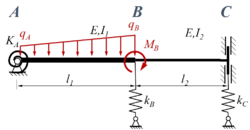
Gesucht ist die analytische Lösung für den Euler-Bernoulli-Balken.
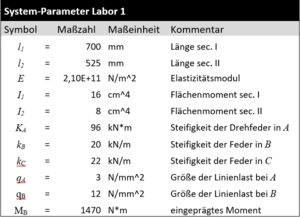
Ermitteln Sie für ein Euler-Bernoulli-Modell die analytischen Verläufe der Schnittgrößen und Verschiebungen im Balken für diese Parameter:
Lösung mit Maxima
Die Aufgabe ist ein klassisches Randwertproblem:
- zwei Gebiete, in denen ein Euler-Bernoulli-Balken in AB und BC durch eine Streckenlast q belastet ist (in Bereich II ist die Streckenlast allerdings Null) und somit durch die Differentialbeziehungberschrieben wird.
- Rand- und Übergangsbedingungen in den Punkten A, B, C
Wir verwenden xi und ξi als Koordinaten je Bereich, in der Übersicht sieht das Randwertproblem so aus:
| Rand A | Bereich I | Übergang B | Bereich II | Rand C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | |||
 |  | 
|
Header
Diese Aufgabe mit der Methode der Finiten Elemente in KW96 gelöst.
/*******************************************************/
/* MAXIMA script */
/* version: wxMaxima 15.08.2 */
/* author: Andreas Baumgart */
/* last updated: 2017-09-06 */
/* ref: TM-C, Labor 1 */
/* description */
/* */
/*******************************************************/
Declarations
Wir definieren die Parameter
- .
und die Formfunktionen für die Streckenlast
- .
/* system parameter */
units : [mm = m/1000, cm = m/100];
params : [q[A]=3*N/mm, l[1]=700*mm, EI[1] = 2.1*10^11*N/m^2 * 3*cm*(4*cm)^3/12];
simple : [l[2] = 3/4*l[1], EI[2] = EI[1]/2,
K[A]=2*EI[1]/l[1], k[C] = 512/229*EI[1]/l[1]^3, k[B] = EI[1]/l[1]^3,
q[B] = 4*q[A], M[B] = q[A]*l[1]^2];
params : append(params,makelist(lhs(simple[i])=subst(params,rhs(simple[i])),i,1,length(simple)));
params : subst(units,params);
/* form - functions */
phi[0](xi) := 1 - xi;
phi[1](xi) := xi;
Formfunctions
In Bereich I und II gilt dieselbe Bewegungs-Differentialgleichung
- ,
die wir durch Integration lösen und dann bereichsweise anpassen.
So gilt für Bereich II: q0 = 0 und q1 = 0.
Die allgemeine Lösung ist mit
... für Bereich I:
... für Bereich II:
- .
/* solve ....*/
dgl : EI[i]*diff(w(x),x,4) = q[0]*phi[0](x/l[i]) + q[1]*phi[1](x/l[i]);
/* generic solution */
displ : solve(integrate(integrate(integrate(integrate(dgl,x),x),x),x),w(x));
sections: [[i=1, %c4=C[1,0], %c3=C[1,1], %c2=C[1,2], %c1=C[1,3], q[0]=q[A], q[1]=q[B]],
[i=2, %c4=C[2,0], %c3=C[2,1], %c2=C[2,2], %c1=C[2,3], q[0]= 0 , q[1]= 0 ]];
/* section I */
define( w[1](x), subst(sections[1],subst(displ,w(x))));
define(Phi[1](x), diff(w[1](x),x ));
define( M[1](x), -EI[1]*diff(w[1](x),x,2));
define( Q[1](x), -EI[1]*diff(w[1](x),x,3));
/* section II */
define( w[2](x), subst(sections[2],subst(displ,w(x))));
define(Phi[2](x), diff(w[2](x),x ));
define( M[2](x), -EI[2]*diff(w[2](x),x,2));
define( Q[2](x), -EI[2]*diff(w[2](x),x,3));
Boundary Conditions
Für die 2*4 = 8 Integrationskonstanten
suchen wir jetzt die passenden Gleichungen aus Rand- und Übergangsbedingungen.
Zur besseren Übersicht nennen wir die Schnitt-Momente und -Kräfte nach den jeweiligen Knotenpunkten A, B, C und fügen als Index ein + / - hinzu, um die Seite (+: rechts vom Knoten, -: links vom Knoten) zu kennzeichnen.
Aus Rand "A"
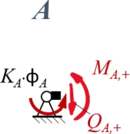
| Geometrische Randbedingungen
Kraft- und Momenten-Randbedingungen |
Aus Übergang "B"
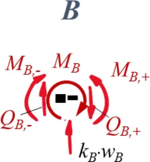
| Geometrische Randbedingungen
Kraft- und Momenten-Randbedingungen |
Aus Rand "C"
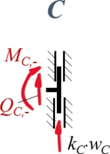
| Geometrische Randbedingungen
Kraft- und Momenten-Randbedingungen |
Und das liefert das Gleichungssystem aus 8 Gleichungen
- .
für die Integrationskonstanten.
/* integration constants */
ICs : [C[1,0],C[1,1],C[1,2],C[1,3],C[2,0],C[2,1],C[2,2],C[2,3]];
/* boundary conditions */
node[A]: [ w[1](0) = 0,
K[A]*Phi[1](0)+M[1](0) = 0];
node[B]: [ w[1](l[1]) = w[2](0),
Phi[1](l[1]) = Phi[2](0),
-Q[1](l[1]) -k[B]*w[2](0) +Q[2](0) = 0,
-M[1](l[1]) -M[B]+M[2](0) = 0];
node[C]: [ Phi[2](l[2]) = 0,
-Q[2](l[2]) - k[C]*w[2](l[2]) = 0];
BCs : expand(append(node[A],node[B],node[C]));
Prepare for Solver
Das Gleichungssystem wollen wir als
schreiben, also
Die Matrix-Elemente sind für die Koeffizientenmatrix
und für die rechte Seite
- .
/* augmented coeff matrix */
ACM: augcoefmatrix(BCs,ICs);
AA : submatrix(ACM,9);
bb : - col(ACM,9);
for i: 1 thru 8 do
print(simplode(["b[",i,"] = ", string(bb[i][1])]))$
for i: 1 thru 8 do
for j: 1 thru 8 do
if not AA[i][j] = 0 then
print(simplode(["A[",i,",",j,"] = ", string(AA[i][j])]))$
Solving
Das Lösen des Gleichungssystems liefert
- .
/* solving */
D : ratsimp(determinant(AA))$
[ P, L, U] : ratsimp(get_lu_factors(lu_factor(AA)))$
cc : ratsimp(linsolve_by_lu(AA,bb)[1])$
sol : makelist(ICs[i] = cc[i][1],i,1,8)$
Post-Processing
Und die Ergebnisse können wir uns anschauen ...
... für w(x):
... für Φ(x):
... für M(x):
... für Q(x):
... für die Lager-Reaktionskräfte:
/* bearing forces and moments */
reactForces: [A[z]=Q[1](0),
M[A] = K[A]*Phi[1](0),
B[z] = k[B]*w[2](0),
C[z] = k[C]*w[2](l[2]),
M[C] = M[2](l[2])];
expand(subst(params,subst(sol, reactForces)));
/* plot displacements */
fcts: [[ w [1](x), w [2](x-l[1])],
[Phi[1](x),Phi[2](x-l[1])],
[ M [1](x), M [2](x-l[1])],
[ Q [1](x), Q [2](x-l[1])]];
facts: [EI[1]/(l[1]^4*q[A]),EI[1]/(l[1]^3*q[A]),1/(l[1]^2*q[A]),1/(l[1]^1*q[A])];
subst(M[B]/l[1]^2,q[A],facts);
textlabels : ["w(x)/(M[B]*l^2/EI[1])→", "w'(x)/(M[B]*l/EI[1])→", "M(x)/M[B]→", "Q(x)/(M[B]/l[1]→"];
for i: 1 thru 4 do(
f : expand(subst(simple,subst(xi*l[1],x,facts[i]*[subst(sol, fcts[i][1]),
subst(sol, fcts[i][2])]))),
f1 : f[1], f2 : f[2],
toplot : [if xi<=1 then f1 else 0,
if xi < 1 then 0 else f2],
plot2d(toplot,[xi,0,1+subst(simple,l[2]/l[1])], [legend, "sec. I", "sec. II"],
[gnuplot_preamble, "set yrange [] reverse"] ,
[xlabel, "x/l[1] ->"],
[ylabel, textlabels[i]]))$
Links
- ...
Literature
- ...